I’ve previously posted about the importance of Drainage Behind a Retaining Wall to minimise the forces acting on the wall…. here is some advice on how to make sure it works.
You should aim to properly drain surface water away from the wall.
Then you need to consider drainage of water in the soil.
There are two sorts of retaining walls as far as drainage is concerned:
Permeable Walls (water can drain through the wall)
Examples of permeable walls are:
- Gravity Block Walls (see this link: Loose laid Retaining Wall Blocks)
- Sleeper Walls (see this link: Sleeper Walls) Unless they have a plastic backing, or no drainage layer!
- Gabions – A steel mesh basket filled with rocks. (see this link Gabions)
With permeable walls the water should seep out anywhere on the face.You still need to put a drainage layer behind the walls. This will ensure that there is a clear path to the seepage points and that any dirt is filtered out rather than staining the face of the wall. It can be worth using a drainage pipe behind the wall as extra security against water pressure building up.
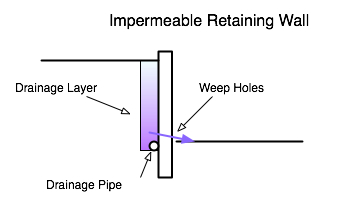
Impermeable Walls (water cannot flow through the wall)
Examples of impermeable walls are:
- Reinforced concrete walls.
- Block Work or Brickwork Walls (see this link: Besser Brick Walls)
- Sleeper walls…. With a plastic backing.
With these walls you need to make special provision for drainage.
Either:
- Weep holes which are specially constructed holes through the structure at 1m, or less, spacing.
or
- An Agricultural Pipe(a perforated or slotted pipe see this Link Aggi Pipe) discharging to a surface water drain. A good idea is where possible have discharge points with silt pits (see this link: Silt Pit) at both ends of the wall.
Drainage Layer
- For the drainage layer I would recommend at least 100mm thickness of 10mm size, or smaller gravel.
- If you are going to have a pipe the width of the drainage layer should be 50-100mm greater than the pipe diameter.
- Isee lots of people use a geotextile round the pipe. In my experience thegeotextile can get clogged with silt and stop the drainage occuring.
For responsibility for Boundary Retaining Walls see Fairness
See Why Aggi Pipes Have Slots In The Base to learn more