Retaining walls are created to hold soil behind them. They can be made to control soil erosion due to hard rains, surround a garden, create a terraced yard, or retain soil along a highway.
When designing a retaining wall, take note that there are several factors that will affect the type of wall and material you build.
These include the following:
Location – it’s best to understand your property lines and your underground as well as above-ground utilities, including stormwater irrigation and management systems.
Soil – the soil that makes the base or foundation of your wall must be checked to determine if it meets the strength needed to support the wall. The bearing capacity of the soil, its type, friction angle, and stress parameters of the soil used for the foundation should be determined. Generally, wet soils, like clay, aren’t suggested for infilling. In locations with freezing temperatures, wet soil can contract or expand, possibly damaging the wall. Sandy soils provide excellent draining.
Design – To start the design, you should calculate the footprint sizes, wall heights, slopes, and setback angle, which depends on the site grade and elevation.
Drainage – Since water is usually the primary reason why retaining walls fail, it’s crucial to ensure that your wall has excellent drainage and there won’t be water buildup behind the wall. It’s best to check the site for drainage patterns and create a drainage system behind the wall. For excavation services, you may contact professionals, such as Hammer Excavations Melbourne, to help you. A good drainage system can include the use of drain pipes, backfilling, or using ‘weep’ holes to let water pass through a wall.
Details
Here are some details I would be using to build a retaining wall with galvanized steel posts up to 800mm high. This is not a guarantee that these details will be suitable for your application.
Ground
I would want to be building it in reasonable ground such as Hard Clay, Compacted Coarse Sand, or Gravel.
It is possible to build walls in poorer ground such as fine sand, soft clay and more loamy soil but specialist advice will be required.
Post Hole
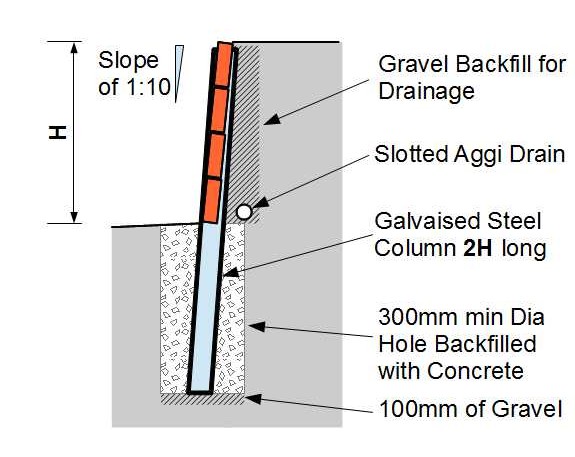
A minimum diameter hole of 300mm dia holes at 1250 spacing (so sleepers cut in half will fit) between posts. Depth to be equivalent to wall height plus 100mm for a gravel layer at the bottom of the hole.
Posts
The minimum post lengths to be twice as long as the final height of the wall.
Set the posts a minimum of 5mm below the planned finished height. It’s safer with the hard steel edges below the softer timber.
Spend some time making sure the tops of the posts are level as any mistakes really show up.
If I was using timber, rather than galvanised steel posts, I would have them on the front face of the wall so the whalings would press against the post.
Drainage
Use an Aggi Pipe with a 100mm gravel surround, maximum stone size of 10mm. Continue the gravel up to just below the surface at least 100mm thick behind the wall. This is to relieve water pressure on the face of the wall. (not to drain surface run off in a storm)
Make sure the ground slopes away from the base of the wall as it helps to keep the soil around the post holes from becoming waterlogged and softening.